An example of how to integrate Mathematics and Science
SHAPE AND DIMENSIONS IN LIVING BEINGS
 |
 |
Does size matter?
- Why are mammals living in cold regions usually bigger than those living in warmer places? Why do mammals living in the mountains usually have short legs and small ears?
- Why does a small mammal have a metabolic rate higher than a bigger one?
- Why does fennec, who lives in Sahara, have big ears?
- Why are the leaves of plants living in dry regions usually thick?
The ratio of skin surface to mass (or, equivalently, the ratio of surface
area to volume) has important consequences for mammals which must maintain
a constant body temperature.
The smaller the surface area is, the smaller the heat production is and then
the slower the metabolic processes are.
- When the animals must avoid losses of heat, they have a small skin surface in comparison with their mass.
- Vice versa, small mammals, having large ratios of surface area to volume, need to produce a great deal of heat in comparison with their size to avoid dying from low body temperature.
- The amount of food and oxygen they must consume is greater in proportion to their size.
- The big
ears of the fennec allow him to lose a great deal of heat.
Similar explanation is applicable to the desert plants, that, in order to keep water, must have a small leaf surface.
From a mathematical point of view… Perimeter : Surface area ratio
The rectangles built with
rubber bunds on the geoboard have the same perimeter (16 units).
What has the largest area?
What the smallest?
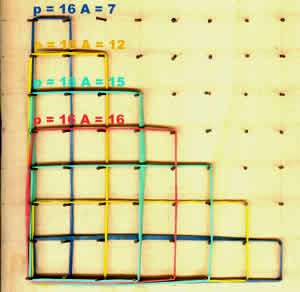 |
Perimeter = 16 units
The unit of area is one square unit enclosed
by four pegs. |
Build all the existing rectangles made with 16 squares of 1 cm2. What
has the longest perimeter? What the shortest?
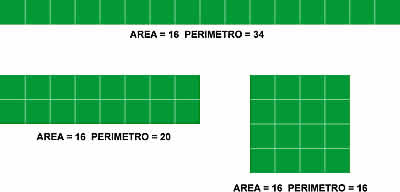 |
Area = 16 units
|
From a mathematical point of view… Surface area : Volume ratio
With 8 wooden cubes, each representing
a volume unit, build all the possible parallelepipeds and measure
the surface of each one (assume the face of a cube unit as
area unit). |
 |
Volume = 8 units
The solid with the largest area is the "longest" parallelepiped
|
With the wooden cubes build 3 cubes of different size and determine
surface and volume of each one.
How does the ratio surface area: volume
vary with the size?
 |
For any given geometric shape (cube, sphere, etc.),
smaller objects have a greater surface to volume ratio than larger
objects. CUBE UNIT --> Area/Volume = 6 |
 |
Two empty cardboard parallelepipeds and a cube have the same lateral surface. In order to compare the volume of the three solids, completely fill them with rice, then weight the rice used for each solid.
|
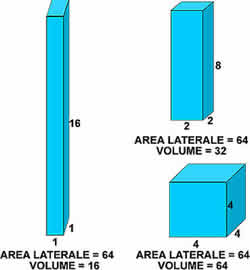 |
Lateral area = 64 units
Among the parallelepipeds, the solid “more
compact” is
the cube, absolutely speaking it is the sphere. |